More projects
Here you can see my projects which for most of them I have publications
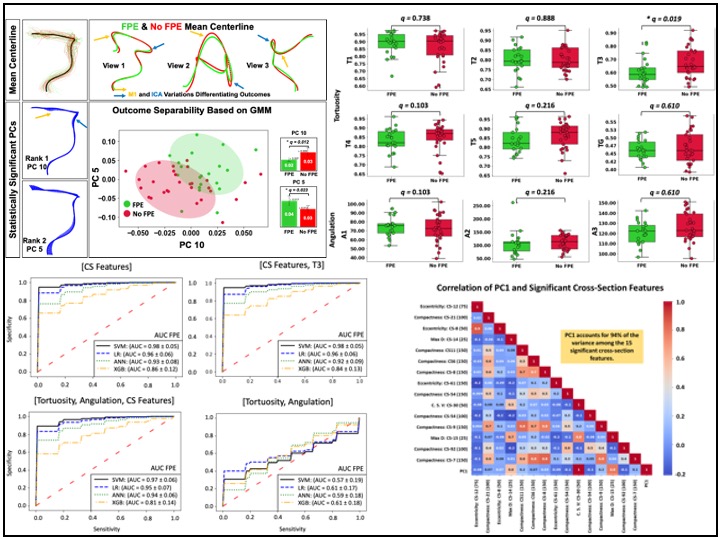
Outcome prediction of Stroke treatment: Statistics, feature Selection, GMM, ML predictions
Statistical analysis and geometric morphometrics were used to explore differences in vascular features between successfull and unsuccessful outcomes. Feature reduction and selection was performed on +5200 features and 14 features were selected as predictors. Machine learning was used to train predictive models of outcome and high accuracy (accuracy = 0.98) was achieved for the best model.
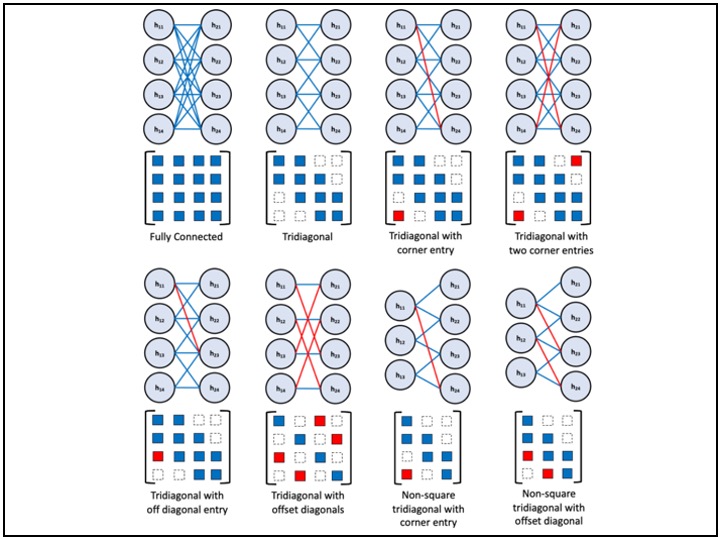
Sparse ANN: A new Sparse ANN and its [pseudo]inverse based training method
A new sparse and structured Neural Network is presented. We introduce a nonsymmetric, tridiagonal matrix with offdiagonal, offset sub, and super-diagonals entries, besides new algorithms for its [pseudo]inverse and determinant calculations. A decomposition for lower triangular matrices is developed to factorize a matrix into a set of matrices that their inverse are straighforward to calculated.
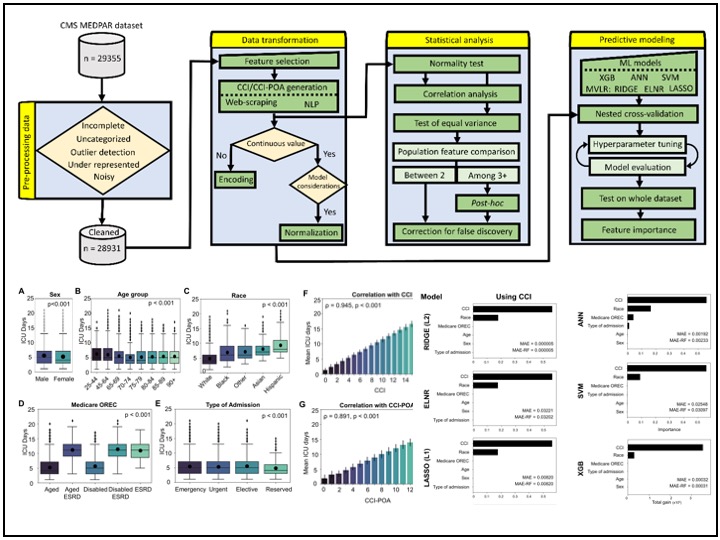
Predicting ICU length of stay: ML predictions, statistical analysis, feature importance and reduction
~30,000 patient data were analyzed. Initial predictors were demographics, admission information, Medicare entitlement, and diagnoses( quantified as Charlson Comorbidity Index, overall & Present on Admission). First, Statistical analysis and feature selections were completed. Next, 7 ML models, including a DL algortihm, were developed and high prediction accuracy achieved.
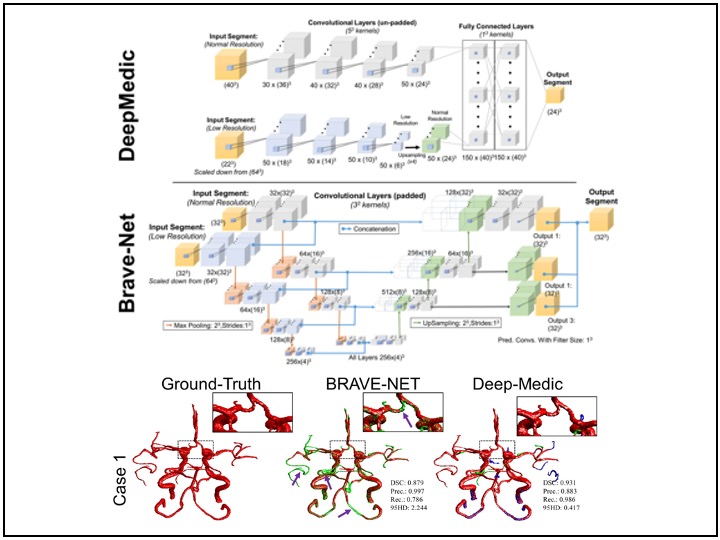
Automated Cerebral vessel segmentation from MR Imaging using CNN
Completed a comparative study between the two context-based 3D CNNs for brain vessel segmentation from MRA. We trained and tested the two models on a dataset of 51 retrospectively collected TOF-MRA images from patients with ICAD. Furthermore, for accurate ground truth generation in small arteries, carotid siphon, and stenotic regions, we employ high-resolution black-blood MRI.
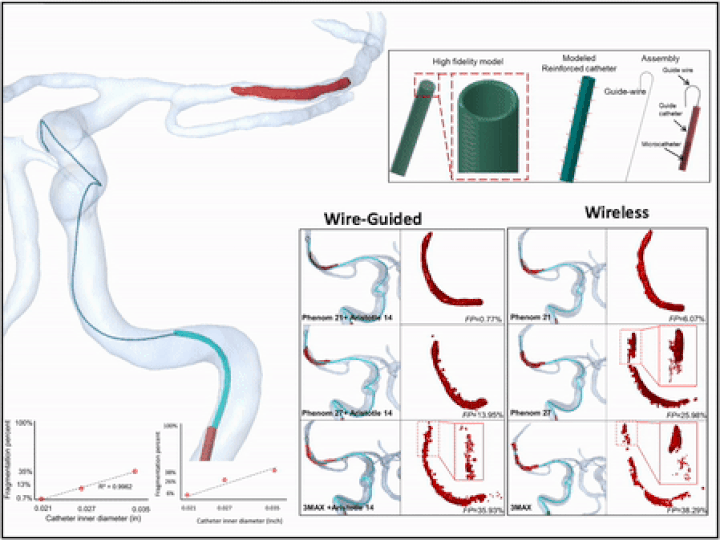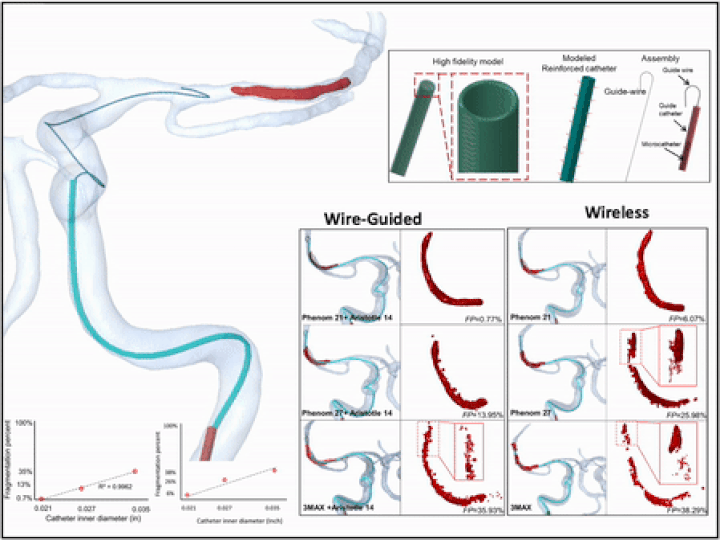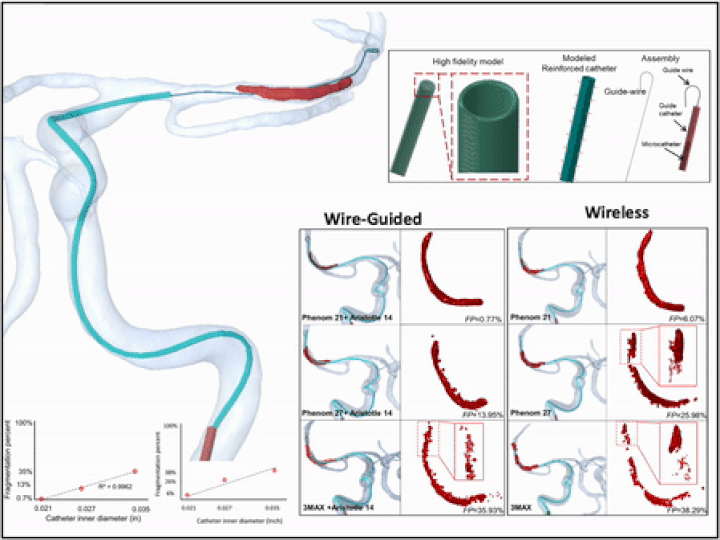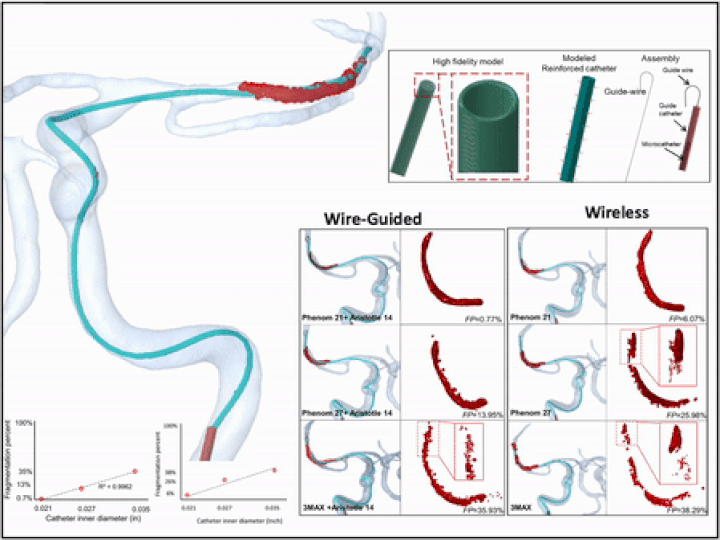
3D virtual wire guided and wireless catheter deployment in modeled real patients
Microcatheter deployment with and without guidewire were simulated using a hybrid FEA- SPH technique. Microcatheters were given a multilayer structure and 3D model was reconstructed from CT images. The fragmentation percentage (FP) of the clot was quantified based on the ratio of converted to non-converted elements in the FEA-SPH method under catheter loading.
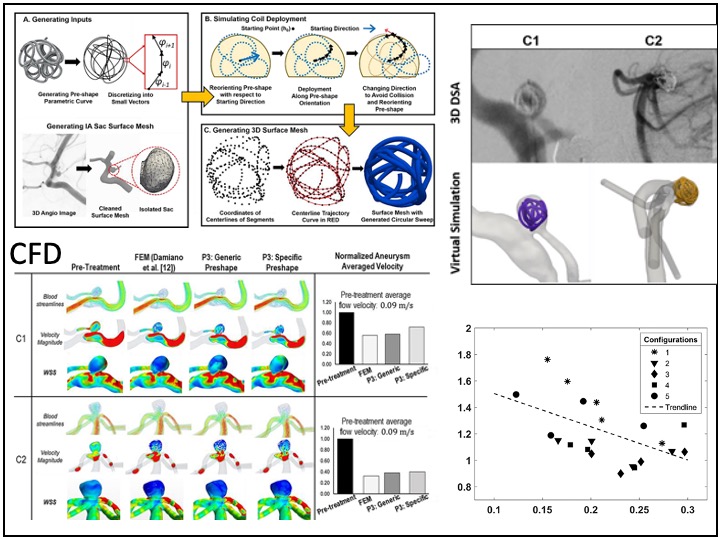
Virtual coiling in modeled patient specific intracranial aneurys and post treatment hemodynamics
To aid in predicting and improving treatment outcome of endovascular coiling of intracranial aneurysms, simulation of patient-specific coil deployment should be both accurate and fast. We developed a fast virtual coiling algorithm and compared it to FEA and preshape ignoring models. Pre and post treatment CFD of blood flow was modeled to investigate performance of the device.
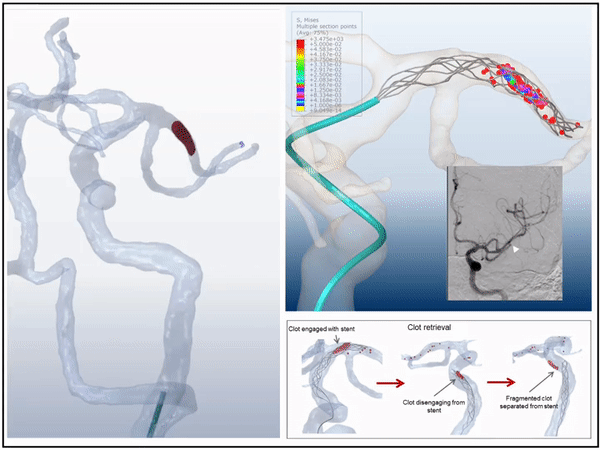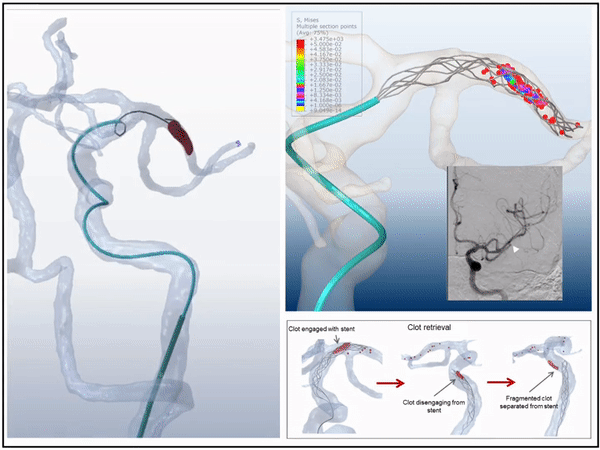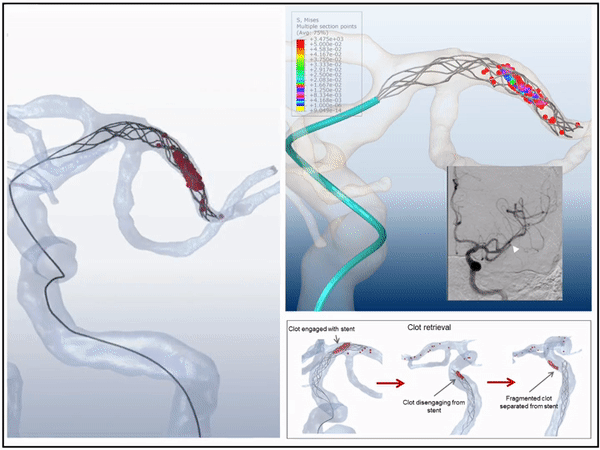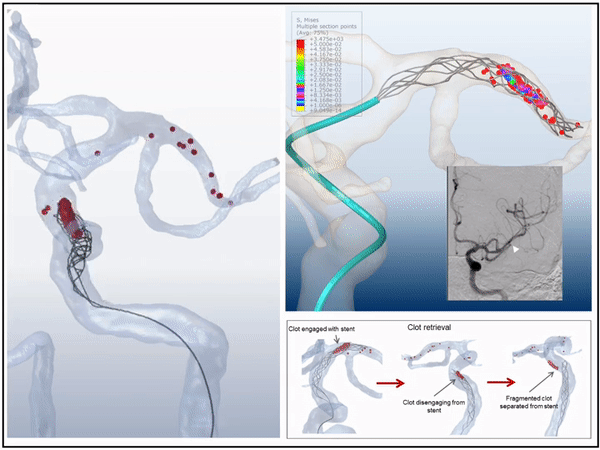
3D virtual simulation stent retriever thrombectomy in modeled real stroke patients
3D simulations of mechanical thrombectomy in modeled patient specific vasculature in presence of the patient's occluding clot we compeleted. The virtual interventions were able to predict the outcome of treatment with high accuracy for both successful and unsuccessful cases. This is the first time that the interaction between blood clot, stent, vessel, and Microcatheter were able to be modeled.
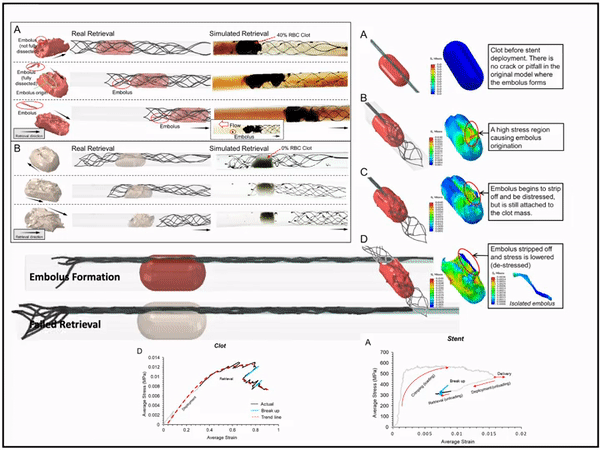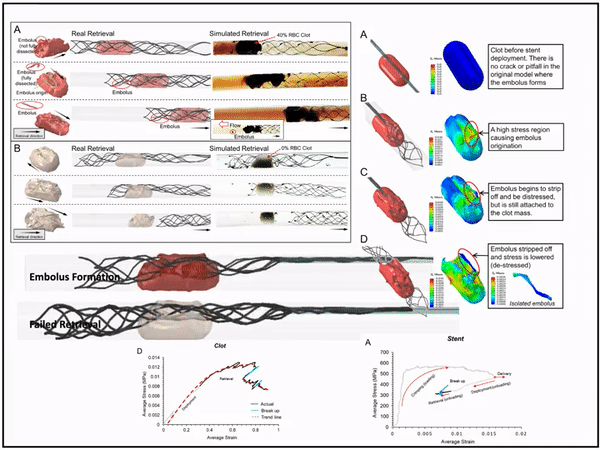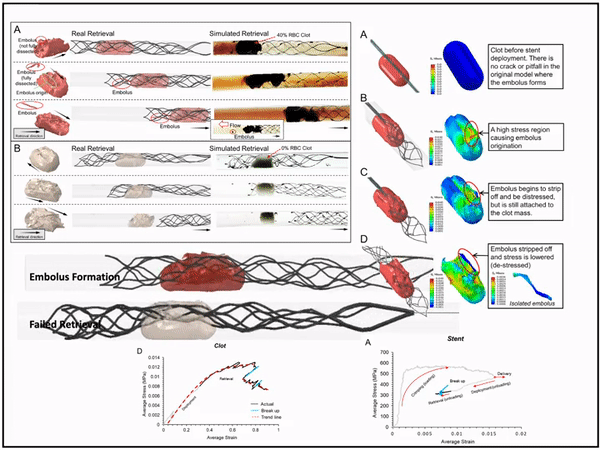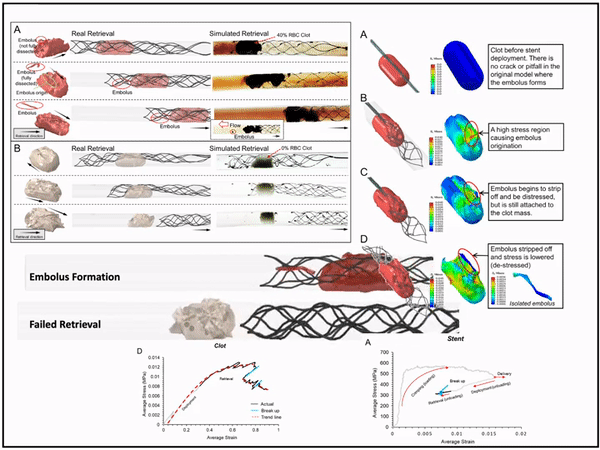
3D modeling of blood clot-stent interaction during mechanical Thrombectomy
I introduced and tested a novel method for modelling blood clots and stent retriever thrombectomy devices which are both practical and accurate in simulating and predicting their behaviour. This method couples and implements both grid-based FEA and meshless SPH to accuractly capture the interaction behavior including disection and fragmentation of clots during mechanical thrombectomy.
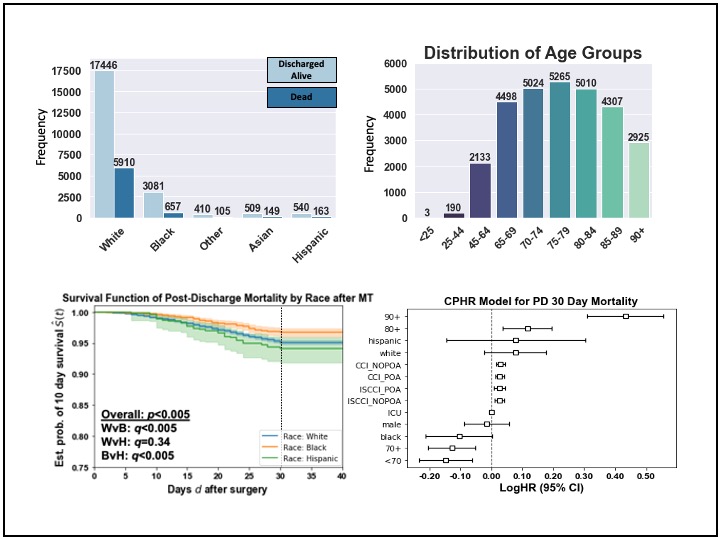
Risk of death afte Stroke treatment: Survival analysis based on race and TPA administration
We completed a survival analysis methods to evaluate risk of mortality after discharge from hospital for Stroke patients. Kaplan Meier was used to measure fraction of patients living for 10, 30, and 90 days after discharge. Log rank test was used to find significantly different race and TPA administration subgroups. Cox hazard proportion was completed to adjust risk evaluation for other confounders like Age.
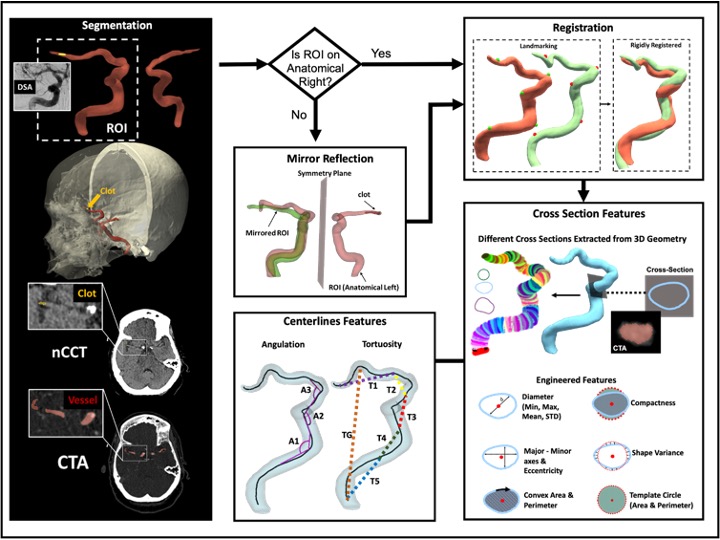
3D image processing: Segmentation, registeration, and I/O program for feature engineering
We analyzed CTA and nCCT from vasculature of stroke patients. Segmentation was completed to generated 3D geometry of the vessels. Rigid and non-rigid registeration to transform cases into the same coordinate system. An symmetry plane and projection alogorithm was developed. An in-house I/O program for feature engineering was developed to extract various features.
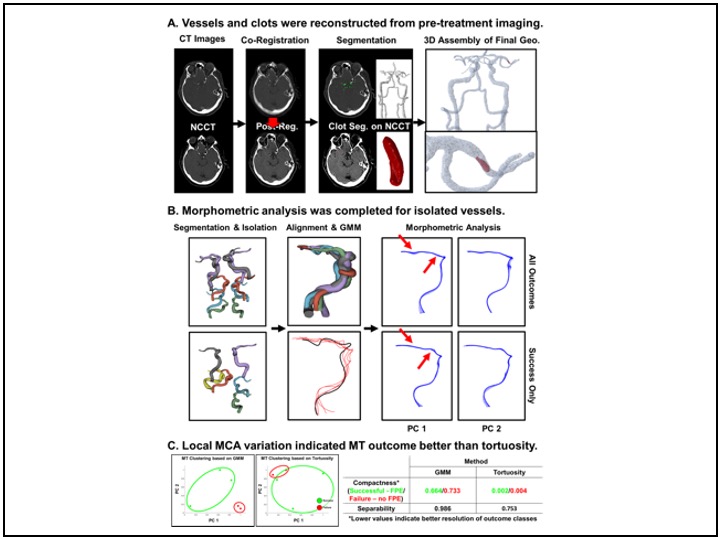
3D vasculature Geometric Morphometrics: Prediction of Mechanical Thrombectomy outcome
Vessels and clots were segmented and reconstructed from pre-treatment CTA and nCCT images. The vasculature were isolated, and centerlines were engineered as curved landmarks. Generalized Procrustes and Principal Component (PC) Analysis were completed, including: image registration, average morphology and landmark variation, and identification of landmarks differentiating MT outcomes.
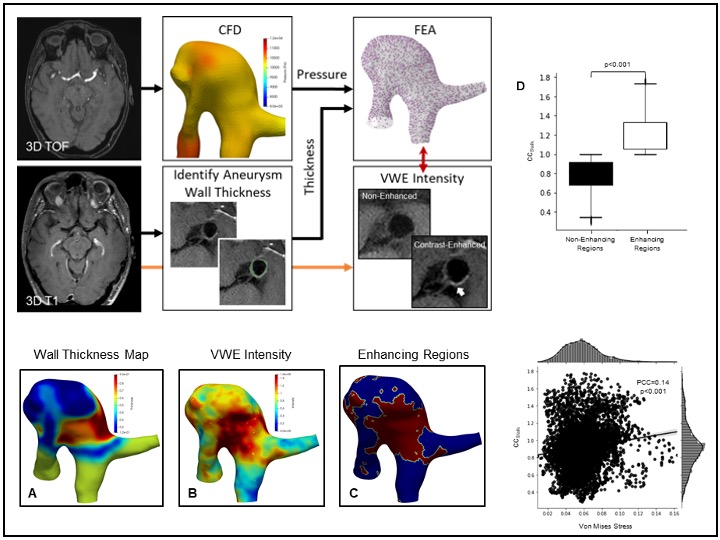
Investigation of correlation between vessel wall enhancement and incresead stress in Aneurysms
TOF-MRA and T1 weighted NE-MRI and CE-MRI were studied in this project. We used the intensity at the genu of corpus callosum for normalization of MRI signal intensity (CCratio). We performed statistical analysis to investigate the differences in stress in enhancing and non-enhancing aneurysm regions. Furthermore, we evaluated the correlation between CCratio and Von-mises stress in the cases.
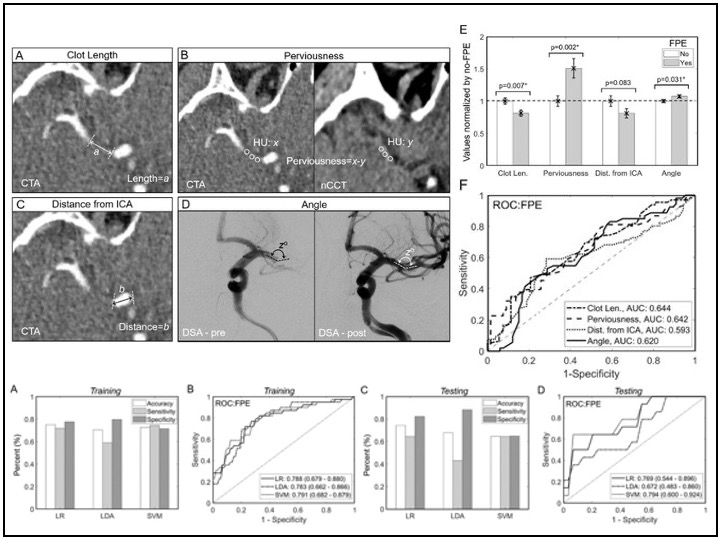
Revascularization outcome prediction for ADAPT) from pre-treatment image features and ML
We created a ML-based model that uses 2D pre-treatment imaging metrics to predict successful outcomes for ADAPT in middle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke cases. In 119 MCA strokes treated by ADAPT, we calculated four imaging parameters. We further built and validated multivariate machine learning models in a random train-test split of our data and the highest accuracy of 74.2% in testing.
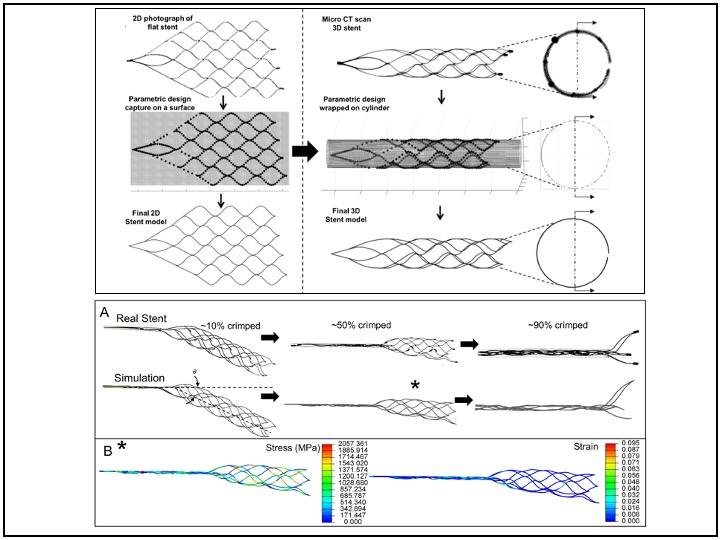
3D parametric model of stents: programming and CAD software, optimization
Solitaire stents were modeled in 2D and 3D with a parametric algorithm that enabled modifying design variables. In this program, cells pattern, size of each cell, number of cells in the stent’s usablelength, and length of the stent for a given number of cells (which automaticallychanges the size of each cell) were created as modifiable parameters that could beinput into the algorithm.
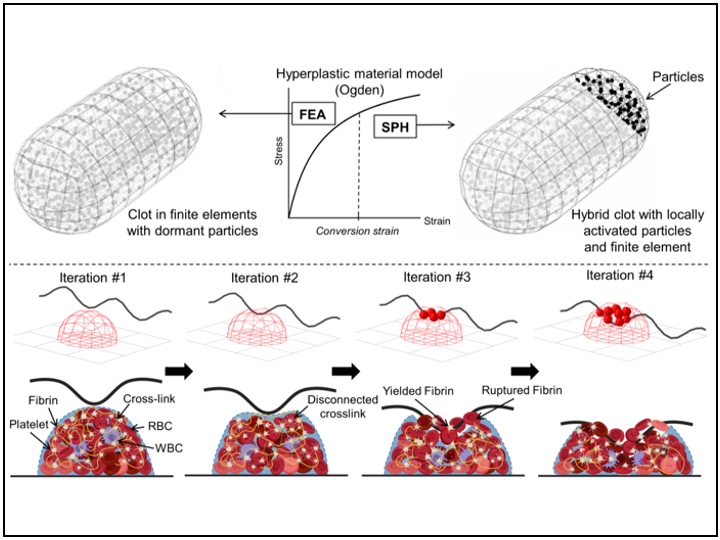
Biomechanics of clot biomaterial: deformation, fragmentation, and dissection
The material properties of the clot were modeled based on the Ogden constitutive equation. To mimic the biological properties of the clot, we implemented a combination of FEA and SPH (Top). The clot is in FEA as the tissue is deflected by the stent struts (first two pictures at the Bottom), but then converts to SPH as the structural fibrin fibers yield and eventually break (last two pictures).
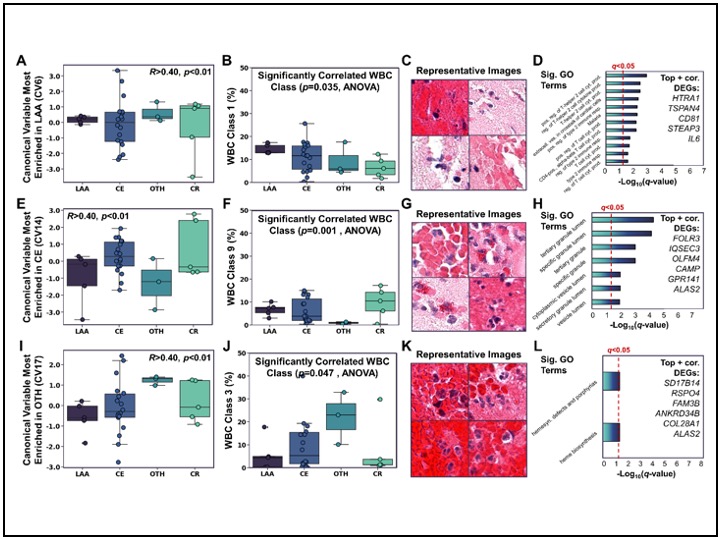
Multi omics data integration for stroke clots using Canonical correlation Analysis
Investigation of etiology biomarkers is an ongoing effort towards stroke secondary prevention. Here, we curated a rare dataset featuring paired transcriptomic and whole-slide histopathology of resected stroke clots. Computational analysis of image and gene features was completed, and canonical correlation analysis was used to identify image-omic correlates enriched in different stroke etiologies.
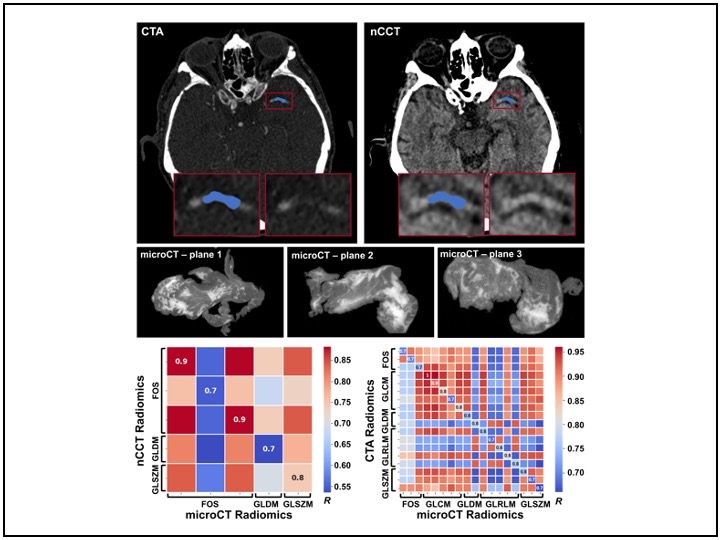
Multimodal CT Imaging and Analysis for identification of scale-invariant Radiomic features
CT imaging is used for stroke diagnosis and treatment (tx) selection. But, resolution of microscopic phenomena that inhibit primary interventions (e.g., NETs and tPA resistance) isn’t possible at pre-tx CT scale. Thus, we completed multimodal CT imaging and radiomic analysis of clots to bridge this gap in scale and identify radiomics correlated among pre-tx imaging (CTA/nCCT) and post-tx pathology (microCT).
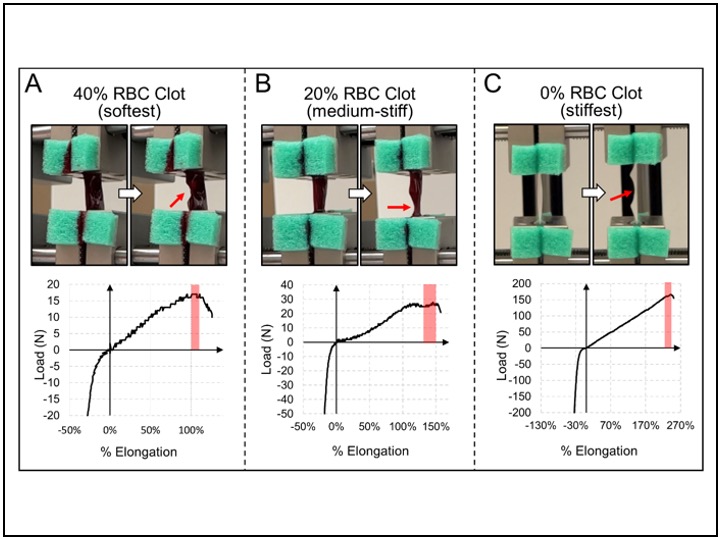
Benchtop tests on synthetic clots with dufferent composition to quantify material behavior
Synthetic clots with different RBC, fibrin platelet, and WBC were generated in the lab. These types represent the most common compositions of the clots. Through these tests we captured some of the most important properties of Stroke causing clots, which were their hyper elastic behavior and their break up points. The data were fit on Ogden constitutive equation of hyper-elastic materials.